Parylene coating
OBANG TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD.What is Parylene coating?
The concept of Parylene coating
Parylene coating is a technology that vaporizes powdery raw materials in a vacuum to form a polymer film layer, and is a coating technology that uses CVD (Chemical-Vapor Depositon).
In the Parylene coating process, the powdered dimer is evaporated by heat, and the evaporated dimer is converted to a monomer through a thermal decomposition unit, cooled before the monomer diffuses into the vacuum chamber, and the cooled monomer is polymerized in the vacuum chamber. A film-type coating film is formed on the object surface.
Since the polymerization reaction of the Parylene coating occurs at a very low pressure and a normal temperature of 30°C or less, it does not generate thermal stress on the surface of the object, and pinholes and pores do not occur because the coating film is formed by a gas-type treatment process.
Unlike the wet coating, the Parylene coating is capable of forming a uniform coating film regardless of the shape even in a product having a complicated shape such as a fine gap, a sharp point, an edge, and a fine hole. Therefore, it is possible to obtain a very useful protective film for products composed of organic and inorganic compounds and organic/inorganic composites.
Parylene coating properties

Immersion or spray
- coating film is non-uniform
(the coating film is thin at the edges and ends) - Pinhole
- Heat deformation
- Mechanical deformation

Parylene coating
- Uniform coating
(uniform at both edges and ends) - No pinhole
- No heat deformation
- No mechanical deformation
- 1Excellent gas barrier (to H2O, O2, etc)
- 2Excellent corrosion resistance
- 3Strong resistance to most chemicals (acids, alkalis and solvents)
- 4High insulation, low dielectric constant and low dielectric constant
- 5Excellent flexibility and mechanical properties at very low temperatures
- 6Excellent radiation resistance in an oxygen-free environment
- 7Almost no out-gassing
- 8Standards such as Mil-I-46058C, IPC-CC-830B, UL94 V-0, FDA Drug and Device Master Files, USP Class VI biocompatibility, and ISO 10993 for medical devices
Configuration of Parylene coating device
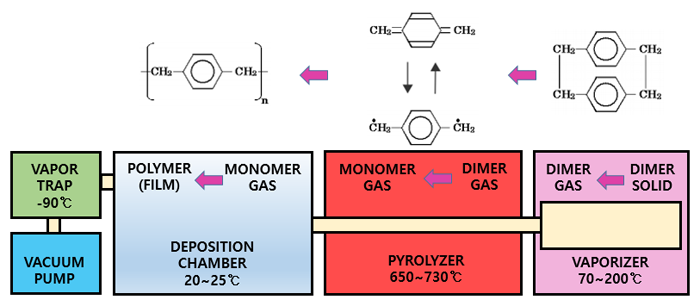
- 1Vaporizer : Apply heat between 80℃~175℃ to make the Parylene dimer evaporate.
- 2Pyrolyzer : Converts gaseous Parylene dimer into monomer by applying high heat between 650℃ and 690℃.
- 3Deposition Chamber : Inside the chamber at room temperature, Parylene is polymerized to coat the surface of the object.
- 4Chiller Trap : It serves to condense the by-products of Parylene generated during the coating process into the cryogenic protection pipe (-70°C to -100°C) so that they do not flow into the Vacuum Pump.
- 5Vacuum Pump : Maintaining the vacuum of the Vacuum Chamber and all connected parts